Quantib Body Composition
The physical state of a patient is relevant in many different areas of healthcare. Body Mass Index (BMI), where the weight is divided by the height in meters squared, is the current clinical standard. However, BMI is a very poor indication of the actual physical state of a patient, because it does not say anything about their muscle mass or fat distribution.
Fully automated segmentation of routinely acquired CT images could therefore be of great help in providing accurate measurements of body composition based on imaging data that is readily available. Various biomarkers based on automatic body composition analysis have shown to be promising prognostic markers in various clinical use cases.
About Quantib Body Composition
Quantib’s body composition algorithm consists of two steps: first, it automatically detects the L3 vertebra from an input CT image and second, it segments the image at the detected L3 level into subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), and skeletal muscle area (SMA), including segmentation of the psoas muscle, the abdominal muscle, and long spine muscles.
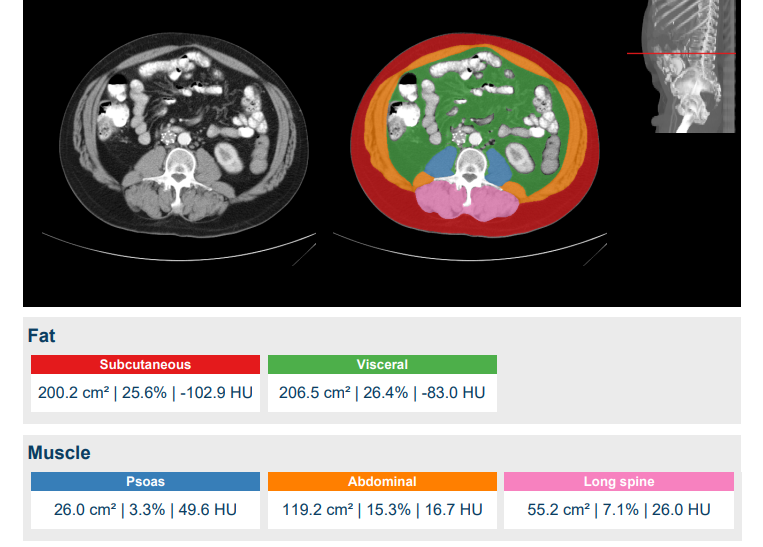
The resulting body composition analysis is presented in a report that indicates the detected L3 slice and shows the segmentation results at that level. It furthermore lists the computed areas and average Hounsfield Units for each of the segmentation classes.
Additionaly, the body composition results can be downloaded in a tabular file that lists all computed descriptors for each of the DICOM series that were processed with the software, to straightforwardly allow further research based on the analysis.
Interested to try out AI-powered body composition measurements on your own CT data? Get in touch!
Publications
Quantib Body Composition is being used in many different fields of research. To discover some of those, check out the already published scientific research that used Quantib Body composition.
Publications